
Welcome to RestraintMaker
RestraintMaker is a tool for MD-simulation restraint preparation. The package can be used to manually pick position - or distance restraints or automatically assign well-spread distance restraint over multiple molecules (e.g., used for dual-topology relative free energy (RFE) calculations). The package can be used either in a scripting mode or with a GUI-based in PyMOL(see [1]).
Introduction
Thanks to recent years’ methodological, software, and hardware improvements, RFE calculations can tackle more and more complex transformations. This development also causes a growing need for more efficient setups of such calculations, namely automatization. We aim to provide a link in the automatization chain which can easily be integrated into python workflows for RFE calculations or used with a GUI in PyMol. RestraintMaker contains a greedy approach to determine good placements of atom distance and/or position restraints based on geometric measures. It can generate distance/position restraints for RFE calculations with a dual state approach, such as TI. Further, it can be used to create distance/position restraints for multistate methods such as Replica Exchange Enveloping Distribution Sampling (RE-EDS) [3,4]. For more details on the history of distance restraints in RFE calculations, the algorithm of RestraintMaker, and an application to the calculation of relative hydration free energies you can check out:
Content
Development
RestraintMaker is split into two parts:
- RestraintMaker
This part is the core of the program. It can be executed as a standalone.
algorithm: restraint selecting algorithms
tools_RDKit: additional functions for filtering or selecting (see [2])
io: writing/importing outputfiles
utils
- Interface PyMOL:
Allows interfacing to PyMOL and generates the GUI-Expierence (see [1])
Installation
You can retrieve the repository from GitHub: https://github.com/rinikerlab/restraintmaker
Install with Anaconda
#!/usr/bash
# 1. Retrieve the repository
git clone https://github.com/rinikerlab/restraintmaker.git
cd restraintmaker
# 2. activate submodules
git submodule init
git submodule update
# 3. generate an Anaconda environment with the environment file and add the repository to its path:
conda env create --file devtools/conda-envs/dev_env.yaml -n restraintmaker
conda develop -n restraintmaker /absolute_path/to/restraintmaker
# 4. Test
conda activate restraintmaker
python examples/example_gui.py
Install via Pymol Plugin Manager should be possible, but not recommended right now :)
GUI Tutorial
GUI Instructions
On the top left you’ll find some helpful instructions and hot keys for RestraintMaker

Optimized Distance Restraints
Start by loading
Please follow the installation instructions above. Then, you can load the pymol GUI with an example system using
python examples/example_gui.py
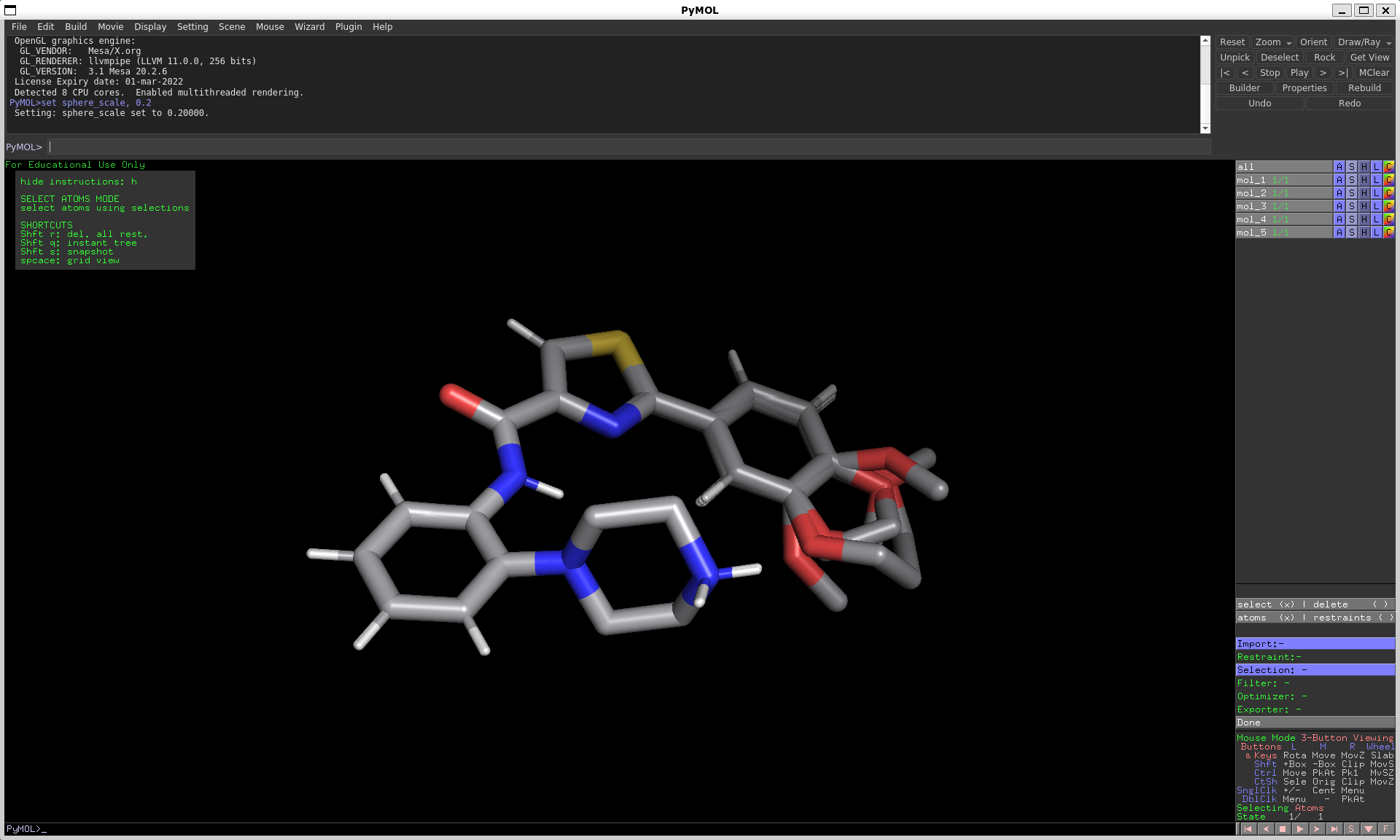
Select & Filter
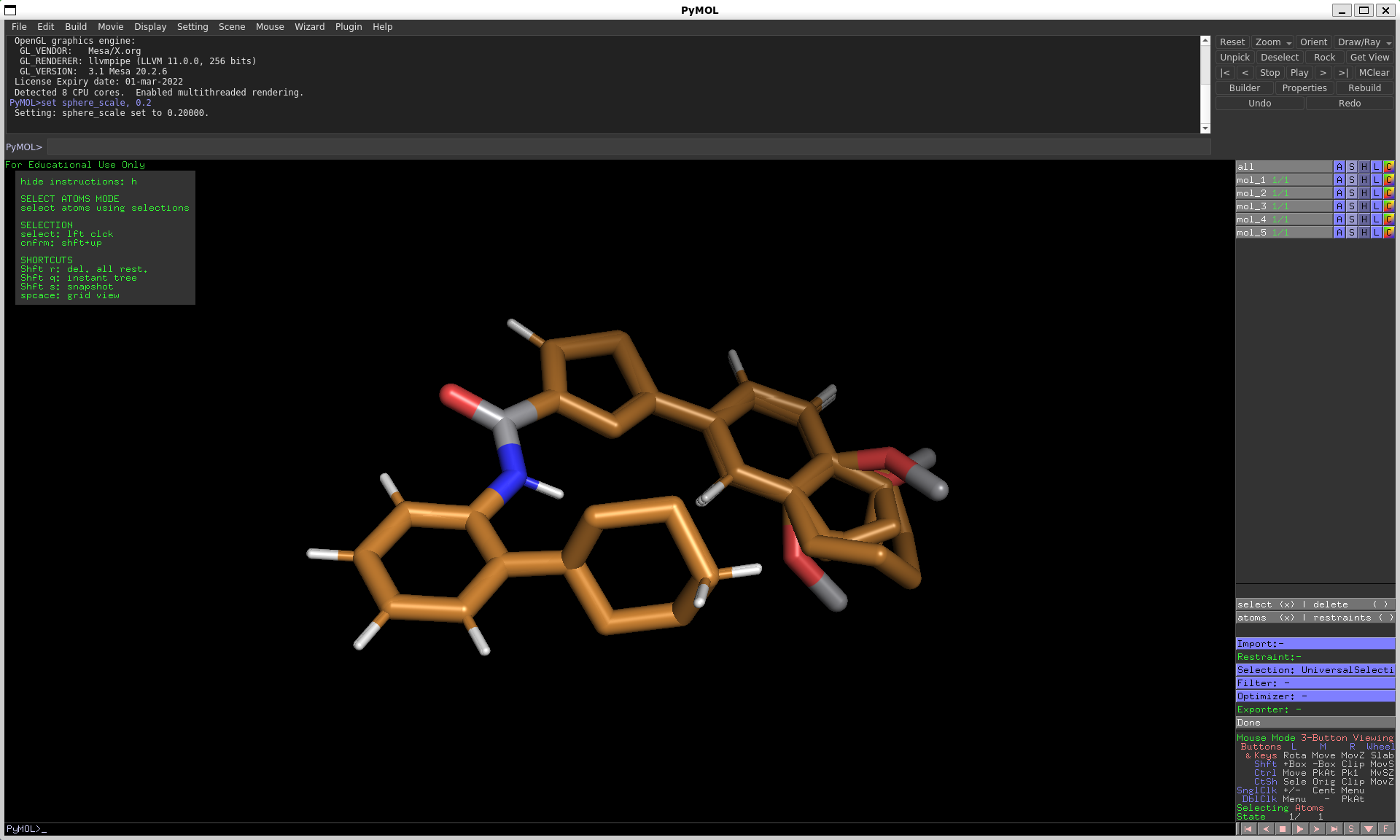
By checking atoms and select in the “Selection Options” of the RestraintMaker menu, you can define which atoms are eligible to be picked for distance restraints. There are several modes to select atoms for this:
SingleAtomSelection: click on an atom to add it to your selectionAllSelection: select all atomsMCSSelection: select the atoms of the maximum common substructure, as found by pymolSphericalSelection: select all atoms within a sphere (see instructions on top left for tips on how to modify the sphere)
After choosing your initial selection, you can modify it by applying filters:
PropertyFilter: submit a pymol Atom property and value to filterElementFilter: specify one or several element typesRingFilter: atoms in rings
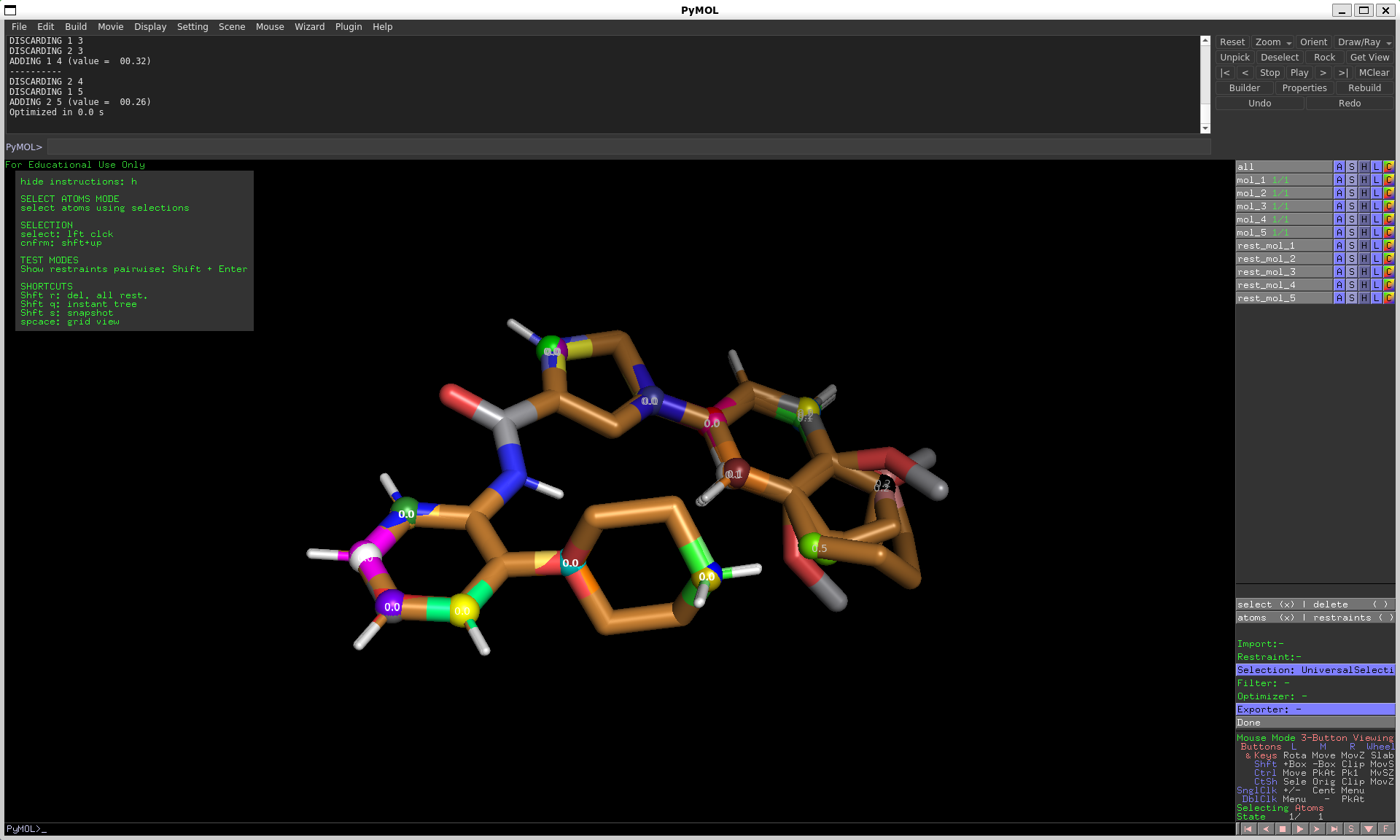
Optimize restraints
To generate the distance restraints, there are two methods:
GreedyGraphOptimizer: the greedy min-max algorithmBruteForceRingOptimizer: brute force approach (optimal solution, but potentially slow)
For both methods you can either use the default parameters or chose your own. Parameters are e.g. the number of restraints to choose per molecule pair.
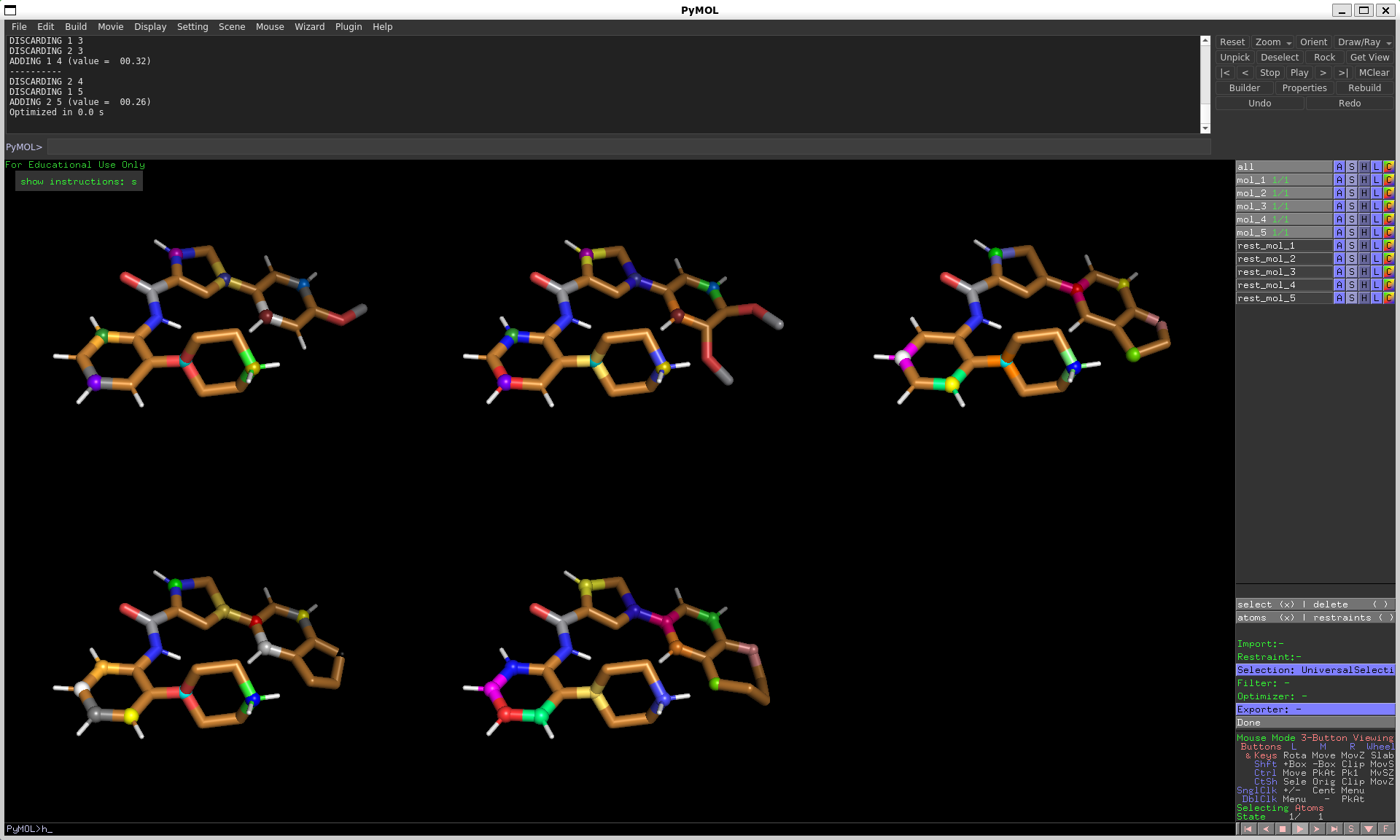
Export restraints to files
After generating your distance restraints, you can export them in one of the following formats:
Gromos_Distance_Restraints: GROMOS formatGromacs_Distance_Restraints: GROMACS formatJSON_Distance_Restraints: JSON format which can be easily parsed and converted to the format of your choice
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank Carmen Esposito and Dominik Sidler for the great discussions. Project based on the Computational Molecular Science Python Cookiecutter version 1.3.
References
[1] The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.5 Schrödinger, LLC. (Anaconda OpenSource Version)
[2] RDKit: Cheminformatics and machine learning software (2021) - http://www.rdkit.org
[3] Christ, C. D.; van Gunsteren, W. F. - Enveloping Distribution Sampling: A Method to Calculate Free Energy Differences From a Single Simulation. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 184110. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2730508
[4] Sidler, D.; Schwaninger, A.; Riniker, S. - Replica Exchange Enveloping Distribution Sam- pling (RE-EDS): A Robust Method to Estimate Multiple Free-Energy Differences From a Single Simulation. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 145, 154114. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4964781
Copyright
Copyright (c) 2021, Benjamin Ries (@SchroederB), Salomé R. Rieder (@SalomeRonja), Clemens Rhiner (@ClemensRhiner) and Sereina Riniker (@sriniker)
